Economic impact of an ageing world: Challenges and Opportunities

Economic impact of an ageing world: Challenges and Opportunities. As the United Nations commemorates the World Day of Social Justice on February 20, we delve into one of the most significant global shifts: the gradual and largely irreversible transition toward an older population. According to the United Nations Population Division, the number of individuals aged 65 and older is projected to double over the next three decades, reaching a staggering 1.6 billion by 2050.
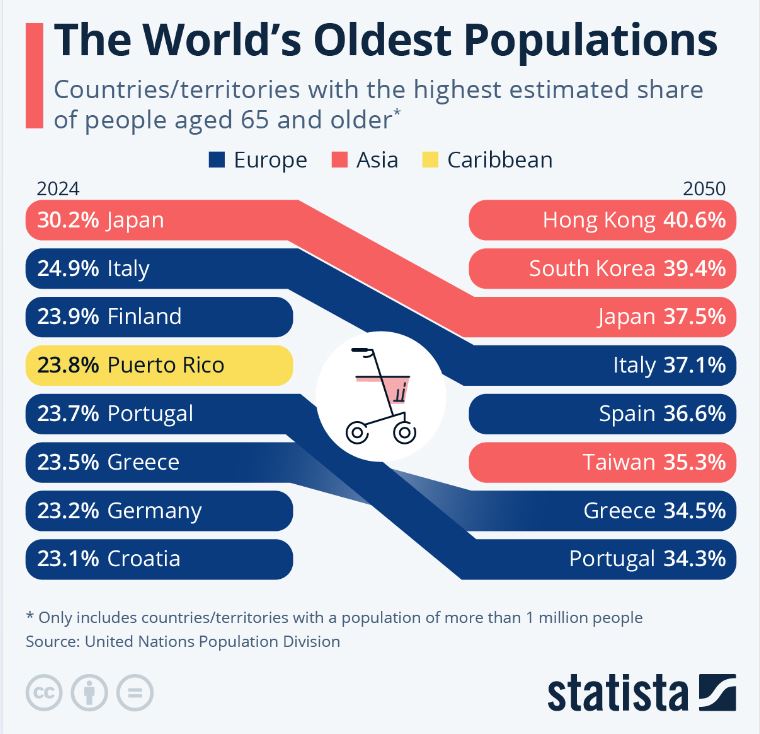
Economic impact of an ageing world: Asia Takes the Lead
Asia stands at the forefront of this demographic trend, with countries like Hong Kong, South Korea, and Japan expected to have the highest share of people aged 65 and older by 2050. While Japan is renowned for its aging population and currently tops the list, other Asian economies are also experiencing a significant shift. Life expectancy has markedly improved over recent decades, contributing to this transformation. By 2050, approximately 40 percent of the populations in Hong Kong, South Korea, and Japan are projected to be 65 and older, a stark contrast to the levels observed in highly developed regions, where the share of older individuals remains in the low 20s.
Population Ageing: A Global Trend
The UN Department for Economic and Social Affairs aptly describes population ageing as a defining global trend of our time. It is both a challenge and a success story. Let’s explore the implications:
Challenges:
- Economic Support: Countries with ageing populations must ensure that their economies can sustain the consumption needs of a growing number of older citizens. This involves:
- Raising the legal retirement age to accommodate longer lifespans.
- Removing barriers to voluntary labor force participation for older individuals.
- Ensuring equitable access to education, healthcare, and work opportunities throughout their lifetimes.
- Healthcare and Well-being: As people age, healthcare demands increase. Providing accessible and quality healthcare services becomes crucial.
- Social Inclusion: Older adults need opportunities for social engagement, preventing isolation and promoting mental well-being.
Opportunities:
- Experience and Wisdom: An older population brings valuable experience and wisdom. Leveraging this knowledge can benefit society as a whole.
- Innovation: Older individuals can contribute to innovation and productivity. Encouraging lifelong learning and skill development is essential.
- Intergenerational Solidarity: Fostering connections between generations promotes mutual understanding and support.
Economic impact of an ageing world: Planning Ahead
Countries in the early stages of this demographic shift have a unique opportunity to plan strategically. Implementing measures such as:
- Social Safety Nets: Strengthening social safety nets to support older citizens.
- Flexible Work Policies: Encouraging flexible work arrangements for seniors.
- Health Promotion: Prioritizing preventive healthcare and healthy aging.
By proactively addressing these challenges and seizing opportunities, nations can navigate the ageing world successfully. Let us celebrate the wisdom and resilience of our older population while ensuring that no one is left behind in this transformative journey. 🌍🌱
References:
- United Nations World Day of Social Justice
- World Social Report 2023: Leaving No One Behind In An Ageing World
- Understanding the Impact of an Aging Society | NIA
Economic impact of an ageing world: Other challenges of an ageing population?

The ageing population presents a host of challenges that societies worldwide must address. Let’s delve into some of these key challenges:
- Healthcare and Social Systems Preparedness:
- Demographic Shift: As the proportion of older individuals increases, health and social systems must adapt to meet their unique needs.
- Increased Demand: Older adults are more likely to experience multiple health conditions simultaneously, necessitating comprehensive healthcare services.
- Geriatric Syndromes: Conditions like frailty, urinary incontinence, falls, delirium, and pressure ulcers become more prevalent.
- Economic Sustainability:
- Supporting Older Citizens: Ensuring that the economy can sustain the consumption needs of a growing number of older people.
- Raising Retirement Age: Some countries consider raising the legal retirement age to accommodate longer lifespans.
- Labor Force Participation: Removing barriers to voluntary labor force participation for older individuals.
- Social Inclusion and Well-being:
- Mental Health: Preventing social isolation and promoting mental well-being among older adults.
- Access to Education and Opportunities: Equitable access to education, healthcare, and work opportunities throughout their lifetimes.
- Resource Allocation:
- Healthcare Spending: Allocating resources effectively to address the changing disease burden associated with ageing.
- Long-Term Care: Providing adequate long-term care facilities and services.
- Income Security: Ensuring old-age income security for retirees.
- Intergenerational Solidarity:
- Connecting Generations: Fostering connections between older adults and younger generations.
- Leveraging Wisdom: Recognizing the value of experience and wisdom that older individuals bring to society.
- Promoting Innovation: Encouraging lifelong learning and skill development.
- Planning Ahead:
- Strategic Measures: Countries in the early stages of demographic shift have an opportunity to plan ahead.
- Social Safety Nets: Strengthening safety nets to support older citizens.
- Health Promotion: Prioritizing preventive healthcare and healthy ageing.
Promoting social inclusion among older adults

Promoting social inclusion among older adults is essential for their well-being and the overall fabric of society. Here are some strategies to foster a sense of belonging and connectedness:
- Intergenerational Interaction:
- Bridge the Gap: Facilitate interactions between older adults and younger generations. Encourage joint activities, such as mentoring programs, storytelling sessions, or collaborative projects.
- School Partnerships: Involve older adults in schools, where they can share their experiences and wisdom with students.
- Community Engagement:
- Age-Friendly Initiatives: Create age-friendly spaces and events that cater to seniors’ interests. These can include cultural gatherings, fitness classes, art workshops, and community gardening.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Encourage older adults to volunteer within their communities. Volunteering provides a sense of purpose and social connection.
- Education and Awareness:
- Early Education: Start educating children about ageing and associated issues from an early age. This helps dispel negative stereotypes and fosters respect for seniors.
- Public Campaigns: Raise awareness about the value of older adults in society through public campaigns and media.
- Consultation and Decision-Making:
- Inclusion in Decision-Making: Involve older individuals in decisions that directly affect them. Consult them on matters related to policies, services, and community development.
- Empowerment: Empower older adults to voice their opinions and contribute to shaping their environment.
- Health and Well-being:
- Health Promotion: Prioritize preventive healthcare and mental well-being. Regular health check-ups and social support networks are crucial.
- Social Clubs and Support Groups: Establish clubs, hobby groups, and support networks where older adults can connect with peers who share similar interests.
- Technology Literacy:
- Digital Inclusion: Provide training and resources to help older adults navigate technology. Access to the digital world enhances social connections.
- Transportation Accessibility:
- Mobility Solutions: Ensure accessible transportation options for older adults. Lack of mobility can lead to social isolation.
Remember, promoting social inclusion isn’t just about addressing challenges; it’s about celebrating the wisdom, resilience, and contributions of our older population. Let’s build a society where everyone feels valued and connected! 🌍🌱
Transformative Technologies Shaping Our Future: A Dive into the Cutting Edge





