
Largest Agricultural Cooperative In The World
Largest Agricultural Cooperative In The World.
Unveiling the Powerhouse: Exploring the Largest Agricultural Cooperative in the World
Introduction: Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating world of agriculture and shine a spotlight on the largest agricultural cooperative in the world. Agriculture is a cornerstone of our society, and cooperatives play a vital role in supporting farmers and promoting sustainable practices. Join us as we take a closer look at this powerhouse organization, its impact on global agriculture, and the key factors contributing to its success.

Agricultural Cooperative
Agricultural cooperatives are essential entities in the global agricultural landscape. They are cooperative organizations owned and operated by farmers, who come together to achieve common goals, address challenges, and enhance their economic well-being. These cooperatives play a crucial role in supporting farmers and promoting sustainable practices while contributing to the overall development of the agricultural sector.
Function and Core Principles
Agricultural cooperatives function as democratic and member-driven organizations. They operate on the principles of cooperation, solidarity, and mutual assistance. The core principles guiding their operations include:
- Voluntary Membership: Farmers join cooperatives willingly, recognizing the benefits of collective action.
- Democratic Control: Cooperatives practice democratic decision-making processes, where each member has an equal say in the organization’s affairs. Decisions are made through voting or consensus-building.
- Economic Participation: Members contribute to and benefit from the cooperative’s activities. Surpluses are allocated based on the extent of members’ involvement rather than their capital contributions.
- Autonomy and Independence: Cooperatives are independent entities controlled by their members, enabling them to act in the best interests of the farmers they represent.
Benefits to Farmers
- Market Access and Bargaining Power: By pooling resources and collective marketing, agricultural cooperatives help farmers access markets and negotiate better prices for their products. They provide a platform to aggregate supply and increase the market presence of small-scale farmers.
- Risk Mitigation: Cooperatives offer risk management tools, such as collective purchasing of inputs, joint financing, and insurance programs, which help farmers reduce risks associated with agricultural production and market fluctuations.
- Knowledge Sharing and Capacity Building: Cooperatives facilitate the exchange of knowledge, information, and best practices among members. They provide training, technical assistance, and education programs to enhance farmers’ skills, productivity, and competitiveness.
- Shared Resources and Infrastructure: Cooperatives often invest in shared resources and infrastructure, such as processing facilities, storage warehouses, and transportation networks. These collective assets benefit members by reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Collective Advocacy: Agricultural cooperatives represent the collective interests of farmers and advocate for favorable policies, regulations, and supportive measures at local, regional, and national levels. They contribute to shaping agricultural policies that benefit their members and the wider farming community.
Conclusion on Agricultural Cooperative
Agricultural cooperatives offer a cooperative and inclusive model for farmers, promoting collective action, democratic decision-making, and shared resources. By functioning on these principles, they empower farmers, strengthen their market position, mitigate risks, and foster sustainable agricultural practices. The significance of agricultural cooperatives lies in their ability to create a supportive environment that enables farmers to thrive, enhancing the overall resilience and development of the global agricultural sector.
World Cooperative Monitor (WCM) Report
“WCM has released The 2022 World Cooperative Monitor, which presents two separate rankings: the Top 300 based on turnover and the Top 300 based on the ratio of turnover to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. The turnover-to-GDP per capita ratio measures the turnover of the Top 300 cooperative and mutual enterprises in relation to the purchasing power of an economy, providing a way to compare the relative size of enterprises considering different levels of national economic wealth. However, it does not calculate the individual contribution of each enterprise to the national GDP; rather, it assesses the size of the enterprise within its national context.
The data compiled for the 2022 World Cooperative Monitor was collected from the fiscal year 2020. The main sources of data include annual and sustainability reports, existing economic databases, data gathered by national associations, research institutes, and other organizations, as well as a questionnaire designed to directly collect data from enterprises. In recent years, our focus has been on collecting turnover and employment data by searching for annual and sustainability reports from each organization in the Top 300 ranking of the WCM 2019, instead of relying primarily on external datasets. This approach ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data.”
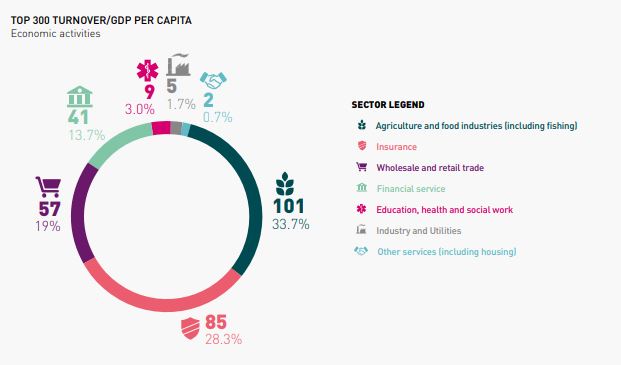
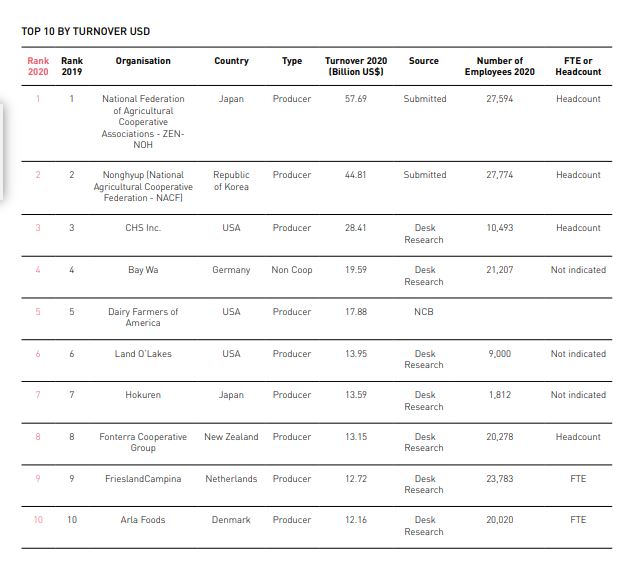
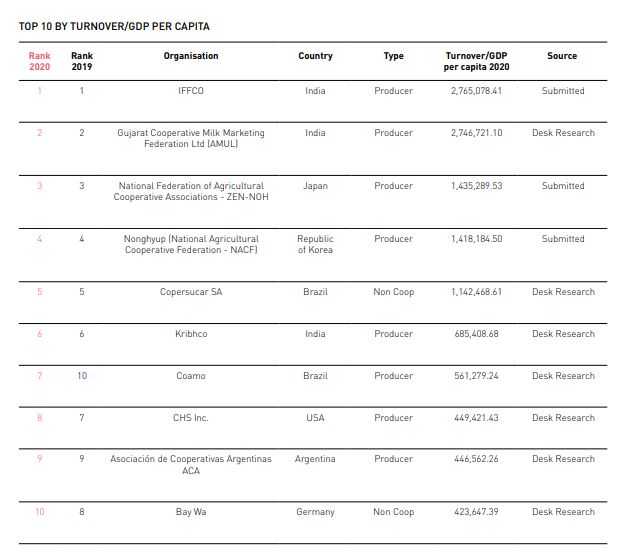
The ranking based on turnover reveals a total of 2,170.99 billion USD for the year 2020 across the Top 300 enterprises. The insurance sector dominates this ranking with 101 enterprises, closely followed by the agricultural sector with 100 enterprises, and wholesale and retail trade with 59 enterprises. On the other hand, the ranking based on turnover over GDP per capita highlights the prominence of the agricultural sector, which boasts 101 organizations. The insurance sector follows with 85 enterprises, and wholesale and retail trade with 57 enterprises. Interestingly, the financial service sector shows greater visibility in the turnover over GDP per capita ranking, with 41 enterprises compared to 26 enterprises in the Top 300 by turnover. It is worth noting that the turnover calculation for the financial services sector in the Top 300 rankings employs slightly different indicators than in the dedicated financial services sector ranking.
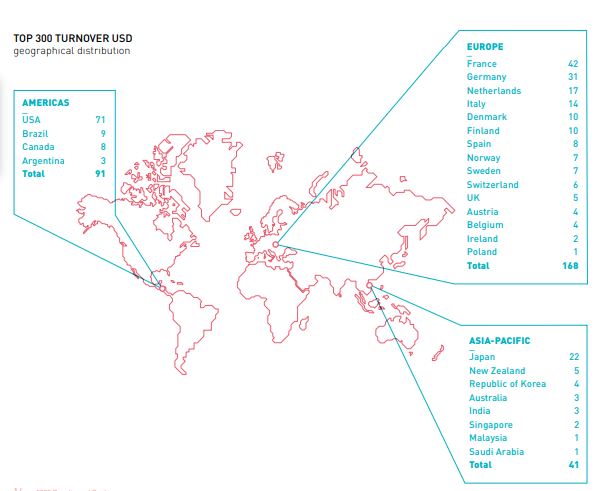
The geographic distribution of both the Top 300 by turnover and the Top 300 by turnover over GDP per capita remains consistent with previous years. The majority of the large cooperatives and mutuals in these rankings are located in the most industrialized countries. However, the Top 300 by turnover over GDP per capita includes a broader range of countries since it is not solely based on absolute value.
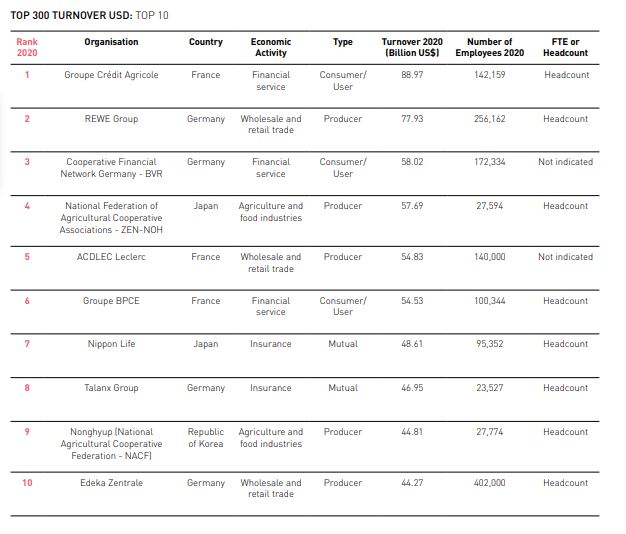
TOP 300 TURNOVER USD: TOP 10
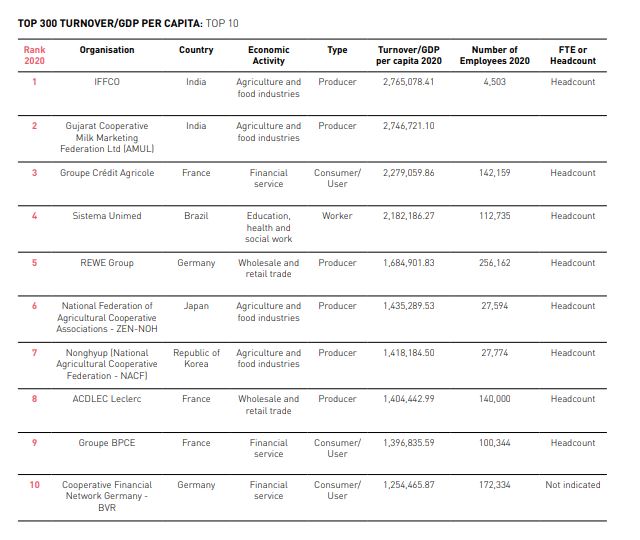
TOP 300 TURNOVER/GDP PER CAPITA: TOP 10
Top Agricultural Cooperative: Agriculture and food industries
These cooperatives encompass the entire agricultural value chain, starting from the cultivation of agricultural products and livestock farming, to the industrial processing of agricultural goods and animals. This sector includes agricultural producers’ cooperatives, as well as consortia of cooperatives or similar arrangements that handle the processing and marketing of agricultural goods for their members. Additionally, organizations in the fishing sector are also considered. Agricultural cooperatives are present in almost every country worldwide. They have a strong presence in both developed and emerging economies and play a significant role in ensuring food security and reducing poverty in various regions. By pooling resources and fostering collective arrangements, these cooperatives assist farmers in increasing their returns and income, promoting economic empowerment within the agricultural community.
TOP 10 Agricultural Cooperative by Turnover USD
TOP 10 Agrucultural Cooperative by Turnover/GDP Per Capita
Global Impact of the Largest Agricultural Cooperative
The largest agricultural cooperative has a significant global impact in several key areas:
- Global Food Security: By supporting farmers and ensuring their economic well-being, the cooperative contributes to global food security. It promotes sustainable agricultural practices, improves productivity, and helps maintain a stable and reliable food supply chain.
- Market Stability and Fair Trade: The cooperative’s activities foster market stability by reducing price volatility and providing fair trade opportunities for farmers. Through collective bargaining and market access, it helps farmers obtain fair prices for their products, ensuring a more equitable distribution of value along the agricultural value chain.
- Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Stewardship: The cooperative plays a vital role in promoting sustainable agriculture practices. It encourages farmers to adopt eco-friendly techniques, reduce resource consumption, minimize environmental impact, and preserve biodiversity. By doing so, it contributes to the long-term sustainability of the agricultural sector.
- Rural Development and Poverty Alleviation: The cooperative’s initiatives support rural development by providing farmers with access to financial services, technology, and training. By improving farmers’ livelihoods, it helps alleviate poverty in agricultural communities and stimulates economic growth in rural areas.
Role in Shaping Agricultural Policies
The largest agricultural cooperative wields influence in shaping agricultural policies at national and international levels. It represents the collective voice of farmers and advocates for their interests. The cooperative engages in policy dialogues, participates in regulatory discussions, and collaborates with governmental and non-governmental organizations to develop policies that support farmers, promote sustainable agriculture, and ensure food security.
Influence on the Overall Industry
The cooperative’s influence extends beyond its direct activities. It sets industry standards for sustainable practices, quality assurance, and social responsibility. By showcasing successful models of cooperative agriculture, it inspires other farmers and organizations to adopt similar approaches, leading to positive changes in the overall industry.
Future Outlook: Agricultural Cooperative
The largest agricultural cooperative has a promising future with potential for growth and impact. However, it faces certain challenges in an ever-changing agricultural landscape:
- Technological Advancements: Embracing emerging technologies, such as precision farming, digital platforms, and data analytics, will be crucial for the cooperative to enhance productivity, efficiency, and market access. It must keep pace with technological advancements to remain competitive.
- Climate Change and Resource Scarcity: Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, affecting crop yields, water availability, and overall sustainability. The cooperative must adapt to changing climatic conditions and develop strategies to mitigate risks, build resilience, and promote climate-smart agriculture.
- Market Dynamics and Global Trade: Global trade policies, market trends, and consumer preferences can significantly impact the cooperative’s operations. Adapting to evolving market dynamics and meeting changing consumer demands will be essential for maintaining competitiveness and market access.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations with governments, international organizations, research institutions, and other stakeholders will enable the cooperative to leverage collective knowledge, resources, and expertise to address complex agricultural challenges and drive positive change.
By navigating these challenges and embracing opportunities, the largest agricultural cooperative can continue to lead the way in promoting sustainable agriculture, shaping policies, and contributing to global food security and rural development in the years to come.
Largest Commercial Banks in US





