Battery Swapping Technology for EV's
Battery Swapping Technology for EVs.Battery swapping is a process where electric vehicle batteries that have been depleted are replaced with fully charged ones.
How does Battery Swapping Technology work.
The process is quite similar to refueling a gasoline vehicle at a gas station. The aim of battery swapping technology is to eliminate the need for drivers to wait for a long time while their electric vehicles charge, which can take several hours. This would help address the issue of range anxiety, which is a common concern among electric vehicle drivers.
There are two main methods of battery swapping: automated and manual. Automated battery swapping involves a robotic system that automatically removes the depleted battery from the electric vehicle and replaces it with a fully charged one. This process takes only a few minutes and is done without the need for human intervention. Manual battery swapping, on the other hand, involves a technician who manually removes the depleted battery and replaces it with a fully charged one. This process takes a bit longer than the automated process, but it is still faster than charging an electric vehicle’s battery.
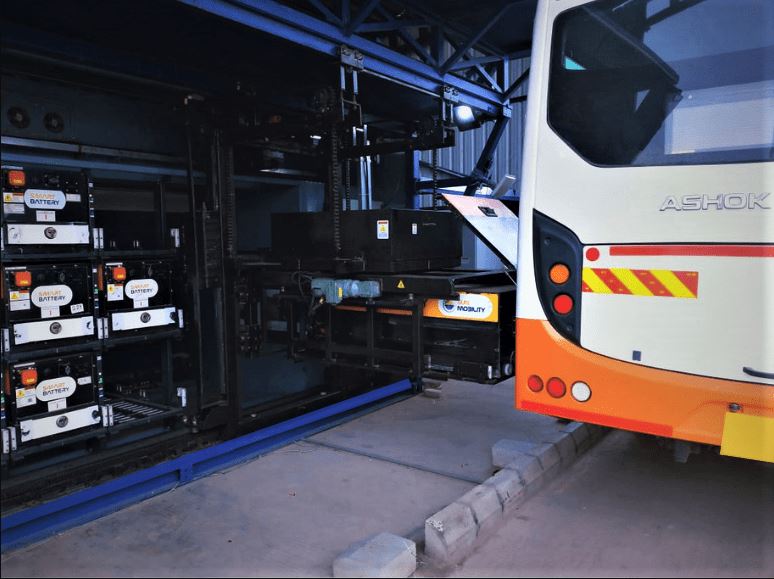

Companies offering Battery Swapping
Several companies have successfully implemented battery swapping technology, including Sun Mobility in India, Gogoro and Ionex in Taiwan, Oyika in Singapore, and Ampersand in Rwanda. These companies offer battery swapping services for different types of electric vehicles, including electric motorcycles, electric scooters, and electric rickshaws.
Overall, battery swapping technology has the potential to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry by addressing range anxiety and reducing the time it takes to recharge an electric vehicle. As more companies adopt this technology, it is likely to become more accessible to electric vehicle owners, making the switch to electric vehicles more convenient and practical for many drivers.
Pros and Cons of Battery Swapping
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to grow in popularity, the question of how to efficiently and quickly recharge their batteries remains a major concern. One potential solution is battery swapping, where depleted batteries are replaced with fully charged ones at a dedicated battery swapping station. Lets explore the pros and cons of battery swapping for EVs.
Pros:
- Faster charging: Battery swapping can be much faster than conventional charging methods. With current charging technology, it can take several hours to fully charge an EV battery, whereas battery swapping can be completed in minutes.
- Convenience: Battery swapping can be more convenient for EV owners who don’t have access to home charging, as it eliminates the need to find a charging station and wait for the battery to charge.
- Extended driving range: Battery swapping allows drivers to quickly replace a depleted battery with a fully charged one, potentially extending the driving range of an EV.
- Reduced battery degradation: Repeatedly fast charging an EV can cause the battery to degrade over time, reducing its overall lifespan. Battery swapping could potentially reduce this degradation by allowing for a more controlled charging process.
Cons:
- Cost: Building a network of battery swapping stations can be costly, and the price of replacing the batteries could be high as well.
- Standardization: Currently, there are no standardized battery sizes or designs, making it difficult to create a universal battery swapping system that would work with all EV models.
- Limited compatibility: Battery swapping may not be compatible with all EV models, as some vehicles may have different battery sizes or configurations that are not interchangeable.
- Storage and maintenance: Battery swapping stations would require a significant amount of space to store and maintain a large number of batteries, which could be costly.
Conclusion:
While battery swapping may offer some benefits, such as faster charging and extended driving range, there are also some significant challenges to overcome. The high cost of building a network of swapping stations and the lack of standardization for batteries are just a few of the obstacles that must be addressed. However, as EV technology continues to evolve, battery swapping could become a viable option for EV owners who prioritize convenience and speed.
Battery Swapping Technology around the world
Battery swapping technology has already been implemented successfully by several companies across the world. Sun Mobility India, Gogoro in Taiwan, Ionex in Taiwan, Oyika in Singapore, and Ampersand in Rwanda are among the prominent names that have successfully integrated this technology into their operations.
Battery Swapping in India

SUN Mobility, a company that provides swappable batteries and infrastructure services for electric vehicles, recently launched its new SwapX battery station and S2.1 battery pack for EVs on January 13. Their goal is to increase the number of battery swapping stations across India using the new compact station, which can be easily installed in small and medium-sized businesses such as pharmacies and department stores.
In an interview with TOI Auto, Chetan Maini, Co-founder and Chairman of SUN Mobility, shared the company’s plan to power up to 1 million EVs in the next two years. Currently, SUN Mobility has more than 210 EV battery swapping points in the country, and these batteries are interchangeable among various types of EVs, including E2W, E3W, and e-Rickshaws.
While most of SUN Mobility’s network is located in the Delhi-NCR region, the new SwapX station could change that significantly. Maini mentioned that EV owners are mainly concerned about the range and charging infrastructure, and with SUN Mobility’s battery swapping technology, they can travel long distances without worrying about range anxiety.
Source: Times of India
Taiwan
Gogoro, a Taiwanese electric scooter manufacturer, has also established a successful battery swapping network in its home country. The company has deployed over 2,000 battery swapping stations in Taiwan, making it one of the largest battery swapping networks in the world. The stations are operated by Gogoro’s own proprietary software, which manages the charging and swapping process seamlessly.

Ionex, another Taiwanese company, has developed a modular battery swapping system that allows for greater flexibility in terms of location and battery capacity. The company has partnered with several scooter and motorcycle manufacturers in Taiwan to offer battery swapping services to their customers.
Singapore
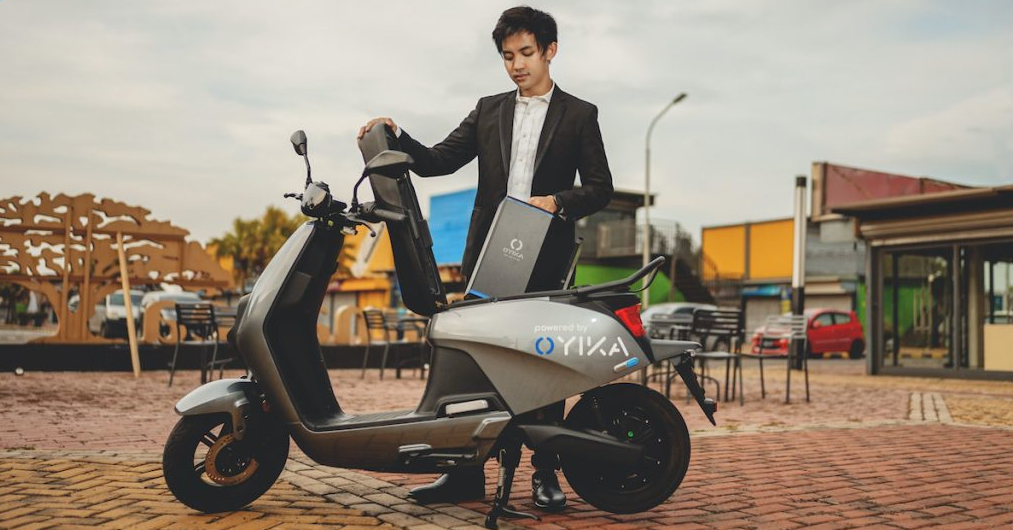

Oyika, a Singaporean startup, has taken a unique approach to battery swapping by using a subscription-based model. The company offers a monthly subscription service that provides access to a network of battery swapping stations across Singapore. The service is currently available for e-bikes and e-scooters, and the company plans to expand its offerings to other types of EVs in the future.
Oyika has several pricing plans for its electric motorbikes, including pay-per-use at US$0.05 per minute, weekly prepaid at US$18 per week, and monthly subscription plans at US$72 per month, which all include battery swaps. The concept is similar to telco plans that bundle data and calls with mobile phones. Each battery swap costs US$1 and can cover a range of about 50km, with the option of carrying up to two batteries or swapping more frequently with one. Most trips are short, with daily travel under 30km, and for a 100km range, it costs US$2 for swaps.
Jinsi, a representative of Oyika, calculated that a gasoline motorbike would require three litres of petrol, costing around US$4.50 to travel 100km, while a 100km range on an electric motorbike would cost US$2 for swaps. Despite being cheaper than gasoline motorbikes, Oyika’s monthly subscription plan did not take off in Cambodia in the second half of 2019 due to people’s apprehension towards electric motorbikes. However, in May 2020, Oyika launched a pay-as-you-go ride-share program to make it more affordable and accessible for the public to try electric motorbikes.
Rwanda

Ampersand, a Rwandan company, has developed a battery swapping solution specifically for the electric motorcycle market. The company has deployed its battery swapping stations in several cities across Rwanda and has partnered with several motorcycle manufacturers to offer this service to their customers.
Overall, these companies have demonstrated that battery swapping technology can be an effective solution to the challenges of EV adoption, particularly in regions where charging infrastructure is still developing. As battery technology continues to improve and become more standardized, battery swapping networks are expected to play an increasingly important role in the growth of the EV industry.
EVs in India are surging now – Insight & Surprising facts