
Worlds Happiest Countries
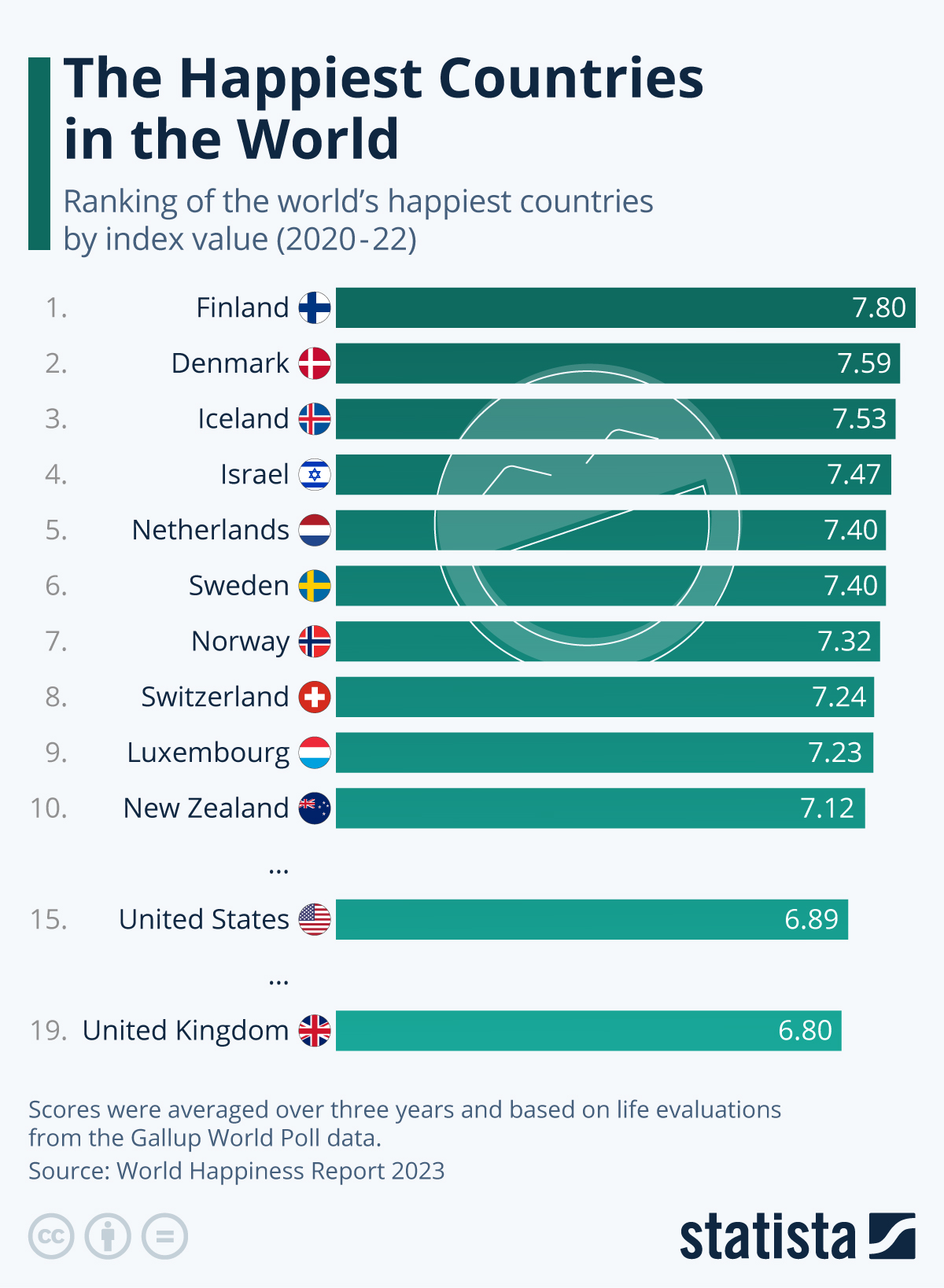
The Ranking Of The World’s Happiest Countries – Spotlight. For the sixth consecutive year, Finland has been named the happiest country in the world according to the 2023 World Happiness Report released on Monday. Although other countries are far behind in terms of scores, a significant portion of the top ten list is dominated by Nordic countries, with Denmark ranking second (7.59), Iceland third (7.53), Sweden sixth (7.40), and Norway seventh (7.32). The United States ranks 15th, while the United Kingdom ranks 19th, having fallen in the rankings for the past four years. The countries with the lowest rankings in the World Happiness Ranking are Zimbabwe (3.20), Sierra Leone (3.14), Lebanon (2.39), and Afghanistan (1.86).

Several critics have raised concerns about the validity of the index for various reasons. Firstly, the use of the term “happiness” is disputed by some who believe that “satisfaction with their lives” would be a more accurate summary, particularly in the case of Finland. Secondly, a Finnish writer highlighted in a 2018 paper that while Nordic countries scored well in terms of factors such as GDP per capita and freedom from oppression, Latin American countries like Paraguay and Guatemala would have been considered the happiest if the index was based on the amount of positive emotions people feel. Furthermore, African countries like Togo and Senegal would have ranked higher if the index measured whether citizens perceive their lives as “meaningful.”
Marwan Bishara, a political commentator at Al Jazeera, has raised doubts about the methodology used to rank countries in the top ten, given the ongoing conflict in Israel and the tight political control in Bahrain, which is ranked fairly high on the list. The 2023 World Happiness Ranking scores were based on a three-year average from 2020 to 2022. Despite the impact of Covid, the war in Ukraine, and rising energy prices and living costs, the figures remained largely consistent with previous years in many countries, with some citizens even reporting higher levels of acts of kindness.
Source: Statista
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at StatistaWorld Happiness Report on its findings on World’s Happiest Countries
The first World Happiness Report was published more than a decade ago, and ten years ago, the United Nations General Assembly declared 20 March as International Day of Happiness. This has led to an increasing number of individuals believing that the well-being of a country’s people should be the benchmark for its success. Additionally, there is a growing agreement about how happiness can be assessed, which means that it is now possible for governments to prioritize national happiness as an operational goal.
What is the prevailing opinion regarding the measurement of national happiness, and what sorts of actions does it demand of people and institutions?
The general consensus for measuring national happiness is to ask a nationally-representative sample of people how satisfied they are with their lives. In order to experience high levels of overall life satisfaction, individuals must also exhibit pro-social, healthy, and prosperous behavior, which Aristotle referred to as “eudaimonia”. However, virtuous behavior doesn’t always result in high levels of life satisfaction for individuals. When assessing a society, situation, or policy, it is important to consider not only the average happiness it brings, but also the scale of misery that results. To prevent misery, governments and international organizations should establish rights, such as those outlined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and broaden the Sustainable Development Goals to consider well-being and environmental policy dimensions jointly. This would ensure the happiness of future generations. When happiness is accepted as the goal of government, the priorities of institutions also shift towards mental health, quality of work, family life, and community. Researchers must evaluate government policies against the touchstone of well-being and address how to promote virtue.
World’s Happiest Countries -How does state effectiveness impact people’s happiness?
The impact of state effectiveness on human happiness is significant. State effectiveness can be gauged by factors such as fiscal capacity, collective capacity, legal capacity, avoiding civil war, and avoiding repression. The average life satisfaction of people is strongly correlated with these measures across countries. Using these measures and income, countries can be classified into three groups: common-interest states, special-interest states, and weak states. Common-interest states have an average life satisfaction that is two points higher than weak states, while special-interest states have an average life satisfaction that is one point higher than weak states. In countries with high average life satisfaction, there is also greater equality in life satisfaction distribution, meaning fewer people experience relatively low levels of life satisfaction.
How does an individual’s act of altruism impact their personal pleasure, the recipient’s happiness, and the general happiness of society?
Assisting others without any expectation of receiving something in return is considered as altruistic behavior. People often engage in different forms of altruistic behavior such as helping strangers, volunteering, donating money, giving blood, etc. There is a direct positive link between happiness and altruistic behavior across individuals and countries. When people assist others, it improves the well-being of both the helper and the receiver. The correlation across countries can be explained by the fact that people who receive help from others usually experience improved well-being. On the other hand, experimental evidence also indicates that voluntary helping behavior mainly motivated by concern for the person being helped can increase the well-being of the individual helper. Moreover, when people’s well-being increases, they tend to become more altruistic. When people experience altruistic help and their well-being improves, they become more likely to help others, creating a virtuous cycle.
World’s Happiest Countries – How accurately can we estimate the current levels of happiness and misery using data from social media?

Can we accurately measure levels of happiness and misery using social media data? Evaluating well-being through social media can provide detailed and timely data on changes in happiness and misery, policy evaluation, and accountability.
Since 2010, advances in social media-based well-being assessments have become more sophisticated. Two main areas of development are data collection and aggregation strategies, and natural language processing techniques to create sentiment models.
Data collection and aggregation strategies have evolved from analyzing random feeds (Generation 1) to analyzing demographically characterized user samples (Generation 2) to the latest digital cohort design studies where users are tracked over time (Generation 3).
Natural Language Processing models have improved in mapping language usage to well-being estimates, progressing from using keyword dictionaries (Level 1) to relying on robust machine learning estimates (Level 2) to using large language models that consider words within their contexts (Level 3).
These improved methods address various biases that affect social media data, including selection, sampling, presentation biases, and the influence of bots.
Digital cohort designs have the potential to provide unparalleled measurements of well-being in time and space, such as monthly subregional estimation. Such estimates can be used to test scientific hypotheses about well-being, policy, and population health through quasi-experimental designs, such as comparing trajectories across matched counties.
Source: Executive Summary of World Happiness Report
Citizenship by Investment Programs
Rising to the Top: Your Guide to Transforming from Manager to Leader






