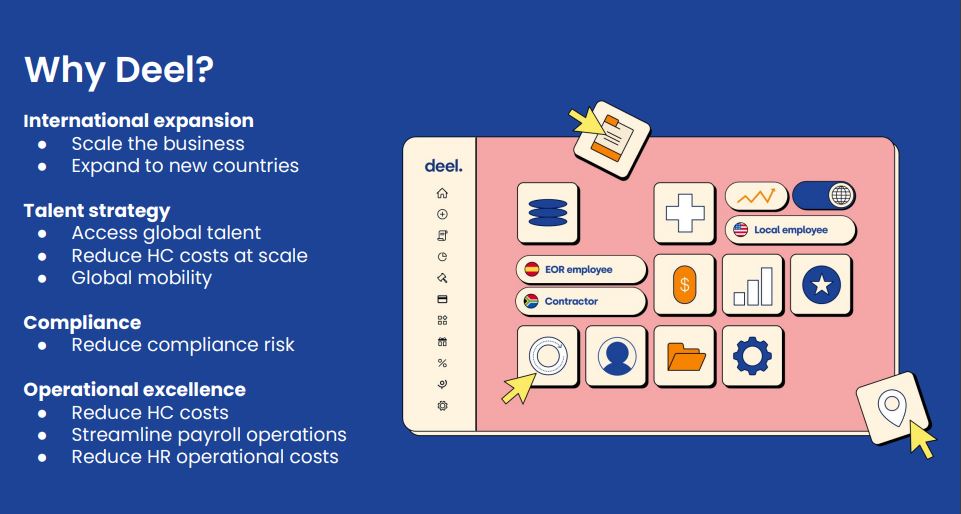
Largest Tobacco Producing States in US
Largest Tobacco Producing States in US & World stats.
The theme of World No Tobacco Day 2023 is “Grow food, not tobacco,” which aims to encourage governments worldwide to cease tobacco growing subsidies and instead provide support to farmers to transition to more sustainable crops that contribute to improving food security and nutrition.
Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), stated that tobacco causes 8 million deaths annually, yet governments across the globe allocate millions of dollars to support tobacco farms. By opting to cultivate food instead of tobacco, we prioritize health, preserve ecosystems, and enhance food security for everyone.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), over 768 million people worldwide suffered from undernourishment in 2021, an increase from 618 million in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic worsened the global food crisis, and the situation was further exacerbated by the conflict in Ukraine, which temporarily disrupted the supply of grains from two major producers in the world market.
Dr. Ruediger Krech, the director of health promotion at the WHO, emphasized that tobacco not only poses a significant threat to food insecurity but also to overall health, including the health of tobacco farmers. Farmers face exposure to chemical pesticides, tobacco smoke, and nicotine levels equivalent to 50 cigarettes, resulting in illnesses such as chronic lung conditions and nicotine poisoning.
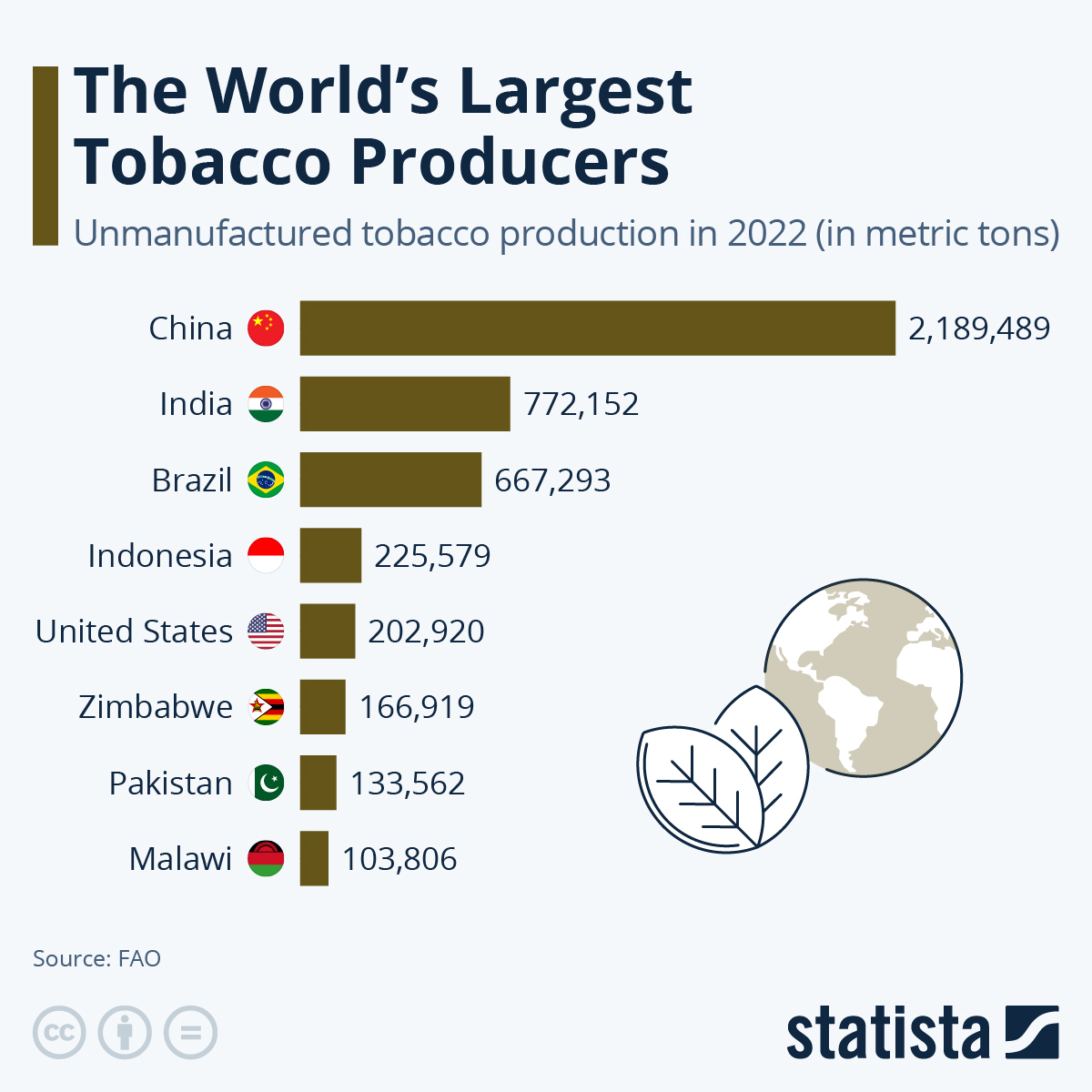 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at StatistaBased on FAO estimates, China is the largest producer of unmanufactured tobacco globally, cultivating 2.1 million tons in 2021. India and Brazil follow closely, each producing approximately 0.75 million tons. Other major tobacco-producing countries include Indonesia, known for its high smoking prevalence, as well as the United States and Pakistan.
Largest Tobacco Producing States in US
According to Statista the following are Top 5 Tobacco Producing States in the US
The rate of cigarette smoking in the United States
The rate of cigarette smoking in the United States has reached an unprecedented low, while the usage of e-cigarettes continues to rise.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the proportion of adults in the United States who smoked cigarettes reached a record low last year. However, the use of e-cigarettes is on the rise.
The latest preliminary data from the National Health Interview Survey, a biannual survey that gathers information on various health-related topics, revealed that approximately 11% of adults reported being current cigarette smokers in the previous year. The survey collected responses from 27,000 individuals aged 18 and above. In 2020 and 2021, around 12.5% of adults indicated that they smoked cigarettes.
This marks a substantial decline compared to the early years when surveys of this nature were conducted. Surveys conducted in the 1940s showed that roughly half of all adults in the US were cigarette smokers. However, smoking rates started to decline in the 1960s. In 2016, 15.5% of adults reported smoking cigarettes.
While recent studies indicate that overall cigarette smoking rates among adults in the United States have decreased, certain groups still face higher risks. The latest survey conducted by the CDC does not provide detailed information on these specific groups. However, the 2023 State of Tobacco Control report from the American Lung Association highlights that cigarette smoking rates remain alarmingly high among communities such as Native Americans, Alaska Natives, and members of the LGBTQ community.
The decline in cigarette smoking among adults in general is expected to have a positive impact on public health. Cigarette smoking continues to be the leading cause of preventable death and disability in the US. According to the CDC, the number of premature deaths caused by smoking surpasses the total number of deaths in all US wars by more than tenfold. Smoking is responsible for 90% of lung cancer cases in the country, and it is also linked to various other serious health issues such as stroke, coronary heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and several types of cancer including bladder, colon, kidney, liver, stomach, and others. Furthermore, individuals living with smokers are also at an increased risk of death due to exposure to secondhand smoke.
The latest survey does not specifically address the reasons behind the decline in smoking rates. However, the downward trend has been observed since the 1960s, following the release of the first report on smoking and health by the US surgeon general. This report conclusively linked smoking to significant health problems.
The decrease in cigarette smoking rates can be attributed to a range of initiatives, according to experts. These include anti-smoking campaigns, educational programs targeting children to raise awareness about the hazards of smoking, stringent laws limiting smoking locations and cigarette advertising, improved availability of smoking cessation programs, and higher taxes that increase the cost of cigarettes.
However, it is worth noting that federal tobacco taxes in the United States have remained unchanged for the past 14 years. The current federal tax on cigarettes stands at $1.01 per pack, while taxes on other tobacco products vary. Additionally, no state has implemented an increase in cigarette taxes during the year 2022.

Shift to e-cigarette
However, there has been a noticeable shift in culture. Smoking is now far less socially acceptable in certain cultures within the United States. On the other hand, e-cigarette use appears to be more socially acceptable, particularly among younger individuals, as studies have indicated. This may explain the increase in e-cigarette usage.
According to the current survey, e-cigarette use rose to nearly 6% last year, up from approximately 4.9% the previous year. Some argue that e-cigarettes can serve as a viable alternative to regular cigarettes, and in some countries, they are even promoted as smoking cessation devices. However, the CDC asserts that “e-cigarettes are not safe for youth, young adults, pregnant women, and adults who do not currently use tobacco products.”
A study published in the BMJ in February found that individuals who used e-cigarettes to quit smoking found them to be less effective than more traditional smoking cessation aids. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) states that there is insufficient evidence to support claims that e-cigarettes are effective tools for smoking cessation. None of these products are approved for this purpose. The FDA also emphasizes that there are no safe tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, vapes, and other electronic nicotine delivery systems. E-cigarettes can generate various chemicals that are detrimental to human health, such as acrolein, acetaldehyde, and formaldehyde, which are known as aldehydes and can lead to lung and heart diseases, according to the American Lung Association.
For teenagers, nicotine exposure can harm the developing brain, as stated by the US surgeon general. E-cigarettes are much more popular among teenagers than traditional cigarettes, indicating that the number of adult e-cigarette users will likely continue to rise.
Separate data from the CDC reveals that approximately 14% of high school students reported using e-cigarettes, while 2% of high school students smoked cigarettes last year. The American Academy of Pediatrics acknowledges that the rate of e-cigarette use among children is alarmingly high.
Specifically, in 2022, nearly 5% of middle school students and around 17% of high school students reported some form of current tobacco use, according to earlier CDC survey data. In 2021, approximately 11% of middle schoolers and 34% of high schoolers stated they had tried tobacco at some point. These statistics on early experimentation with tobacco are significant, as the CDC highlights that the majority of adult smokers began smoking at a young age.
Source : CNN